- Tel: 0086-21-35324116
- E-mail: sales@shenglincooling.com
Introduction
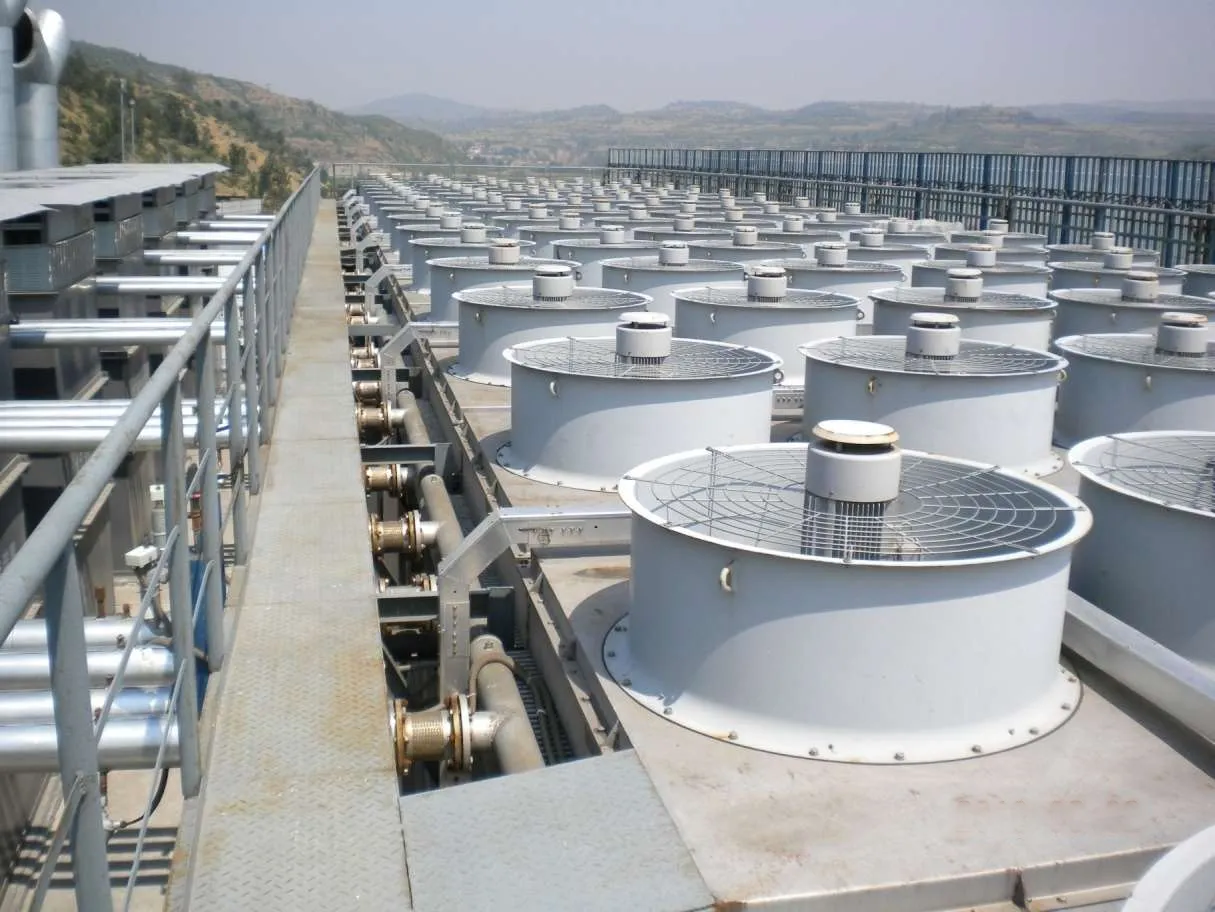
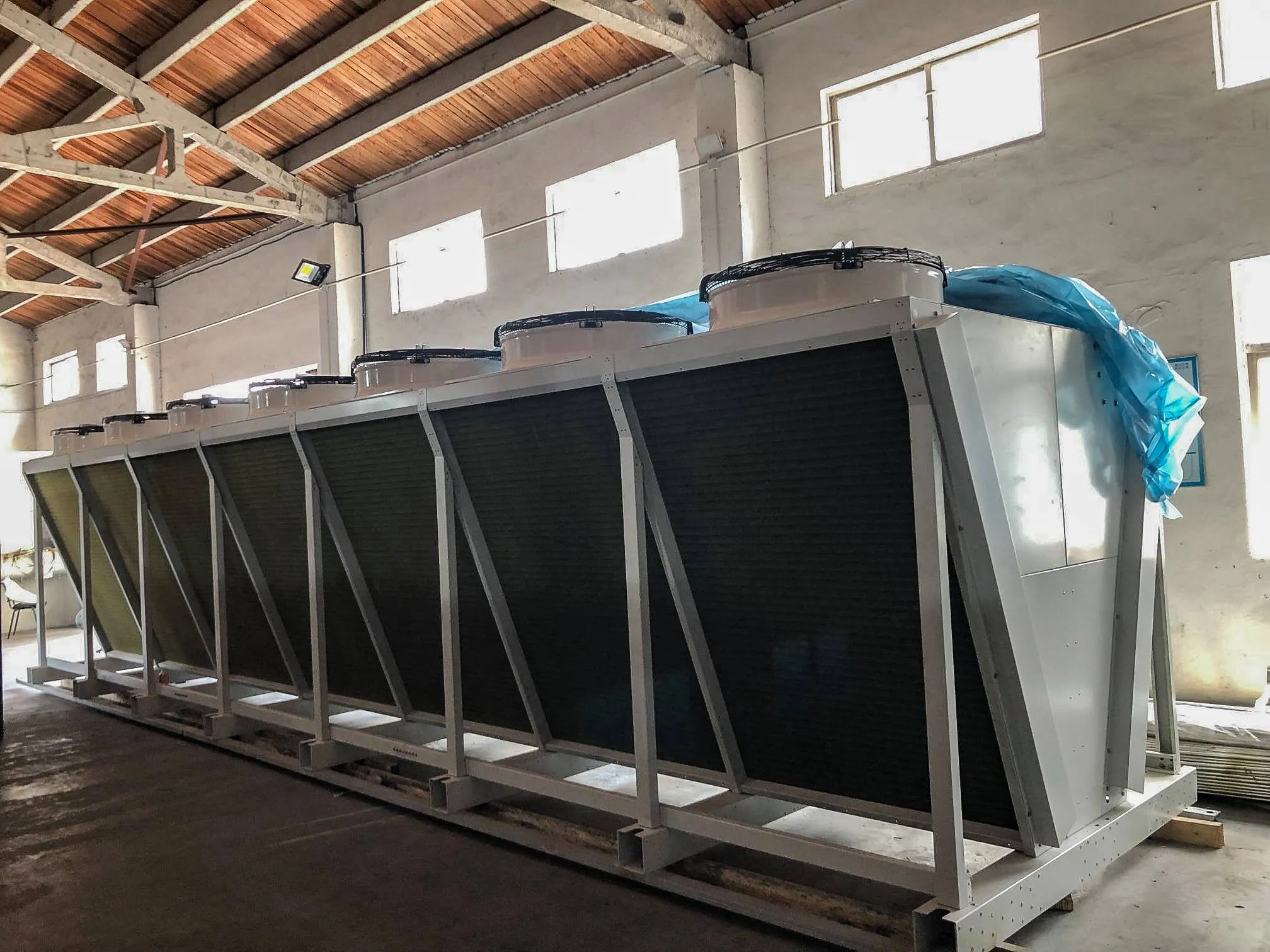
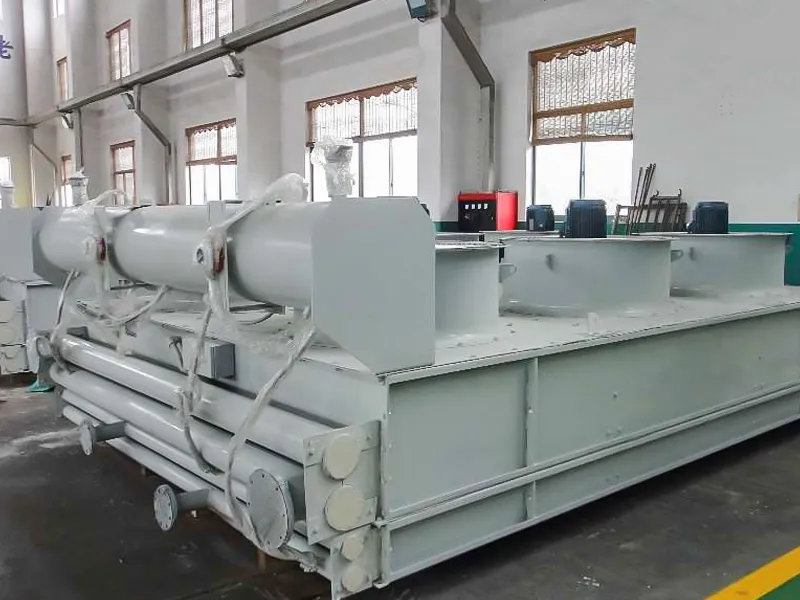
The Air Cooler Tube Bundle is the core heat exchange component of an Air Cooled Heat Exchanger, consisting of finned tubes, tube sheets, baffles, and headers. It enables efficient heat transfer between process fluids inside the tubes and ambient air outside. The bundle is designed for easy removal, inspection, and replacement, ensuring long service life and stable performance in demanding industrial applications.
Technical Specification
| Item | Specification Range | Options / Notes |
| Tube Material | Carbon steel, stainless steel, coppebrass, titanium, alloy steel | ASTM A179, A210, A214, 304/316/321 SS, duplex SS, etc. |
| Tube Outer Diameter (OD) | 12.7 mm – 38 mm (1/2" – 1 1/2") | Customized sizes available |
| Tube Wall Thickness | 1.0 mm – 3.0 mm | According to design pressure |
| Tube Length | Up to 12 m | Special designs on request |
| Tube Type | Plain, finned, internally enhanced | Fin type: L, G, embedded, extruded |
| Tube Sheet Material | Carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel | Forged or rolled plate |
| Tube Sheet Thickness | 20 mm – 100 mm | According to design pressure |
|
Bundle Configuration |
Single-pass / Multi-pass | U-tube or straight tube |
|
Baffles |
Segmental, rod, or customized | Improve turbulence & heat transfer |
|
Design Pressure |
Up to 10.0 MPa (100 bar) | Higher available on request |
|
Design Temperature |
-40°C to +400°C | With alloy tubes up to higher ranges |
| Fin Height | 8 mm – 16 mm | Aluminum, copper, or SS fins |
| Fin Pitch | 250 – 450 fins/m | According to cooling requirements |
| Standards / Codes | ASME, TEMA, API 661, ISO 16812 | CE, PED certification available |
| Maintenance | Removable bundle | Easy cleaning & replacement |
Applications
(1)Power plants – turbine & generator cooling
(2)Oil & gas – compressor, LNG, and pipeline station cooling
(3)Petrochemical & refining – process fluid cooling & condensing
(4)Chemical & metallurgy – process heat exchange
(5)Data centers & industrial HVAC – dry cooling solutions
Advantages
● Eco-Friendly: Zero water consumption, no wastewater discharge.
● Cost-Effective: Lower operational and maintenance costs vs. water-cooled systems.
● High Adaptability: Performs reliably in extreme temperatures and harsh conditions.
● Compact Design: Modular structure for space-saving installations.
● Long Lifespan: Corrosion-resistant materials and robust engineering.
Optional Configurations
● Compliance with ASME and API 661 standards
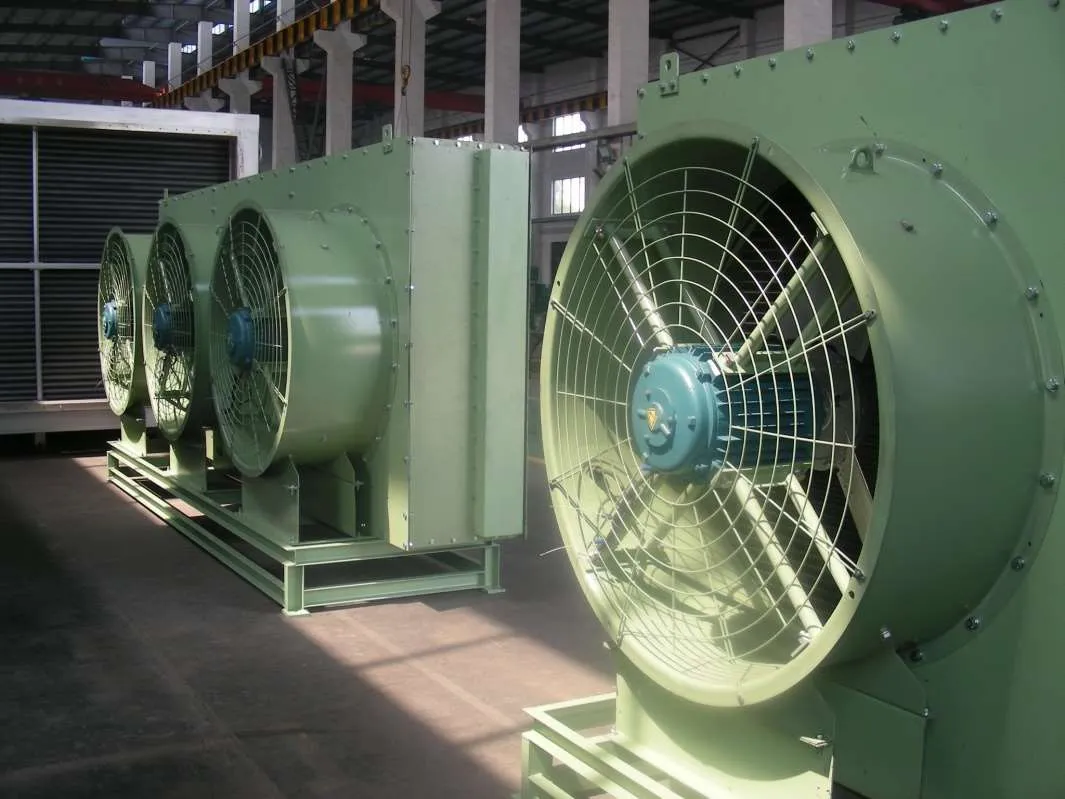
● Forced Draft or Induced Draft fan arrangements
● Horizontal or Vertical air flow design
● Smart Controls (temperature sensors, variable speed fans)
● Explosion-Proof, Low-Noise, or Marine-Grade Designs
● Dry/Wet Hybrid System for Enhanced Performance in high ambient temperatures
● Custom painting & corrosion protection
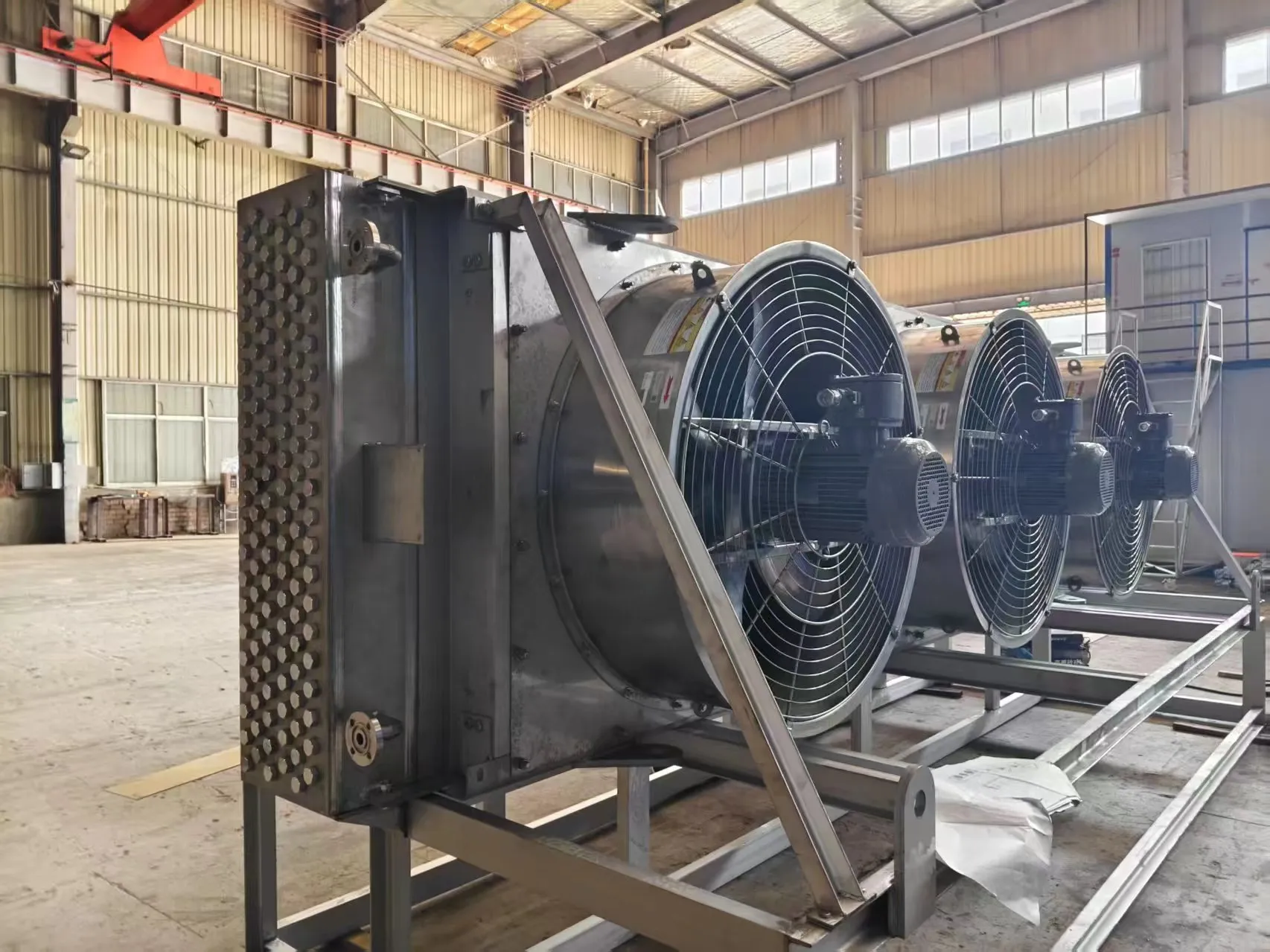
Extended Surface Fin Types Available
● L-foot fin (basic embedded fin, economical and widely used for general-purpose cooling)
● Overlapped L-foot fin (LL type): provides better corrosion resistance by overlapping fin foot over the tube surface
● Embedded G-fin: fins mechanically embedded into the tube surface for improved thermal contact and durability
● Knurled L-foot fin (KL type): uses a knurled surface on the tube to enhance mechanical bonding between fin and tube
● Extruded fin: formed by extruding aluminum over the tube for maximum corrosion resistance and strength, ideal for harsh environments
● Bimetallic finned tubes: e.g., aluminum fins on carbon steel or stainless steel tubes, combining thermal conductivity with structural or corrosion benefits
● Custom fin materials and geometries available upon request
Header Types Available
● Plug-type header (for compact or low-cost design)
● Removable cover plate header (for easy inspection and maintenance)
● Removable bonnet-type header (for higher-pressure applications with external access)
● Manifold-type header (for multi-pass or special flow arrangements)

Country: Thailand

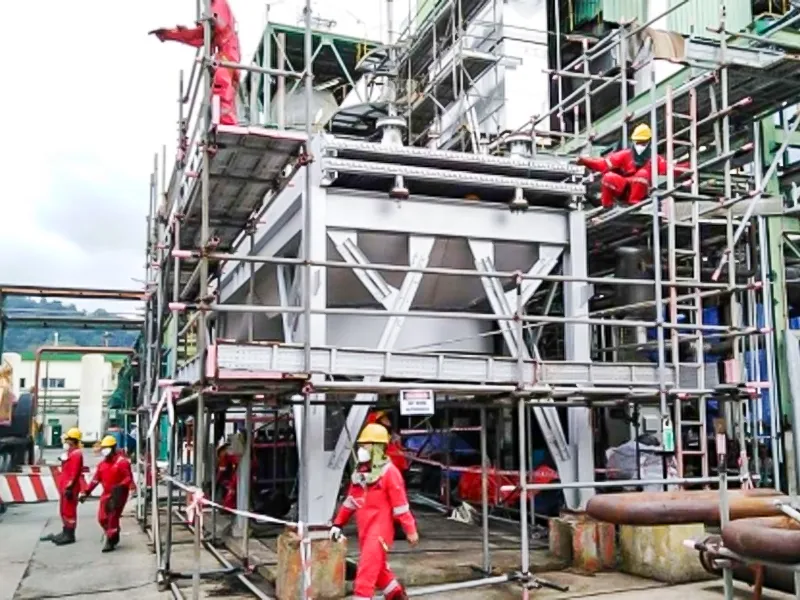
Country: China

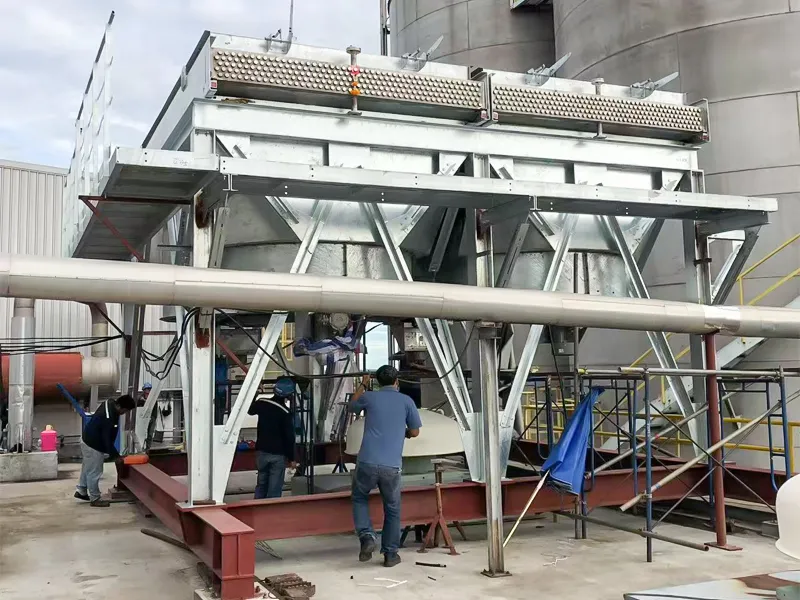
Country: the Philippines
Main Material: Copper Tube/Alu. Fins
Application: Diesel Generator Radiator

Country: China
Caterpillar Engine

Country: Oman

Country: Russia

Country: USA
Main Material: Carbon Steel Tube /Alu. Fins
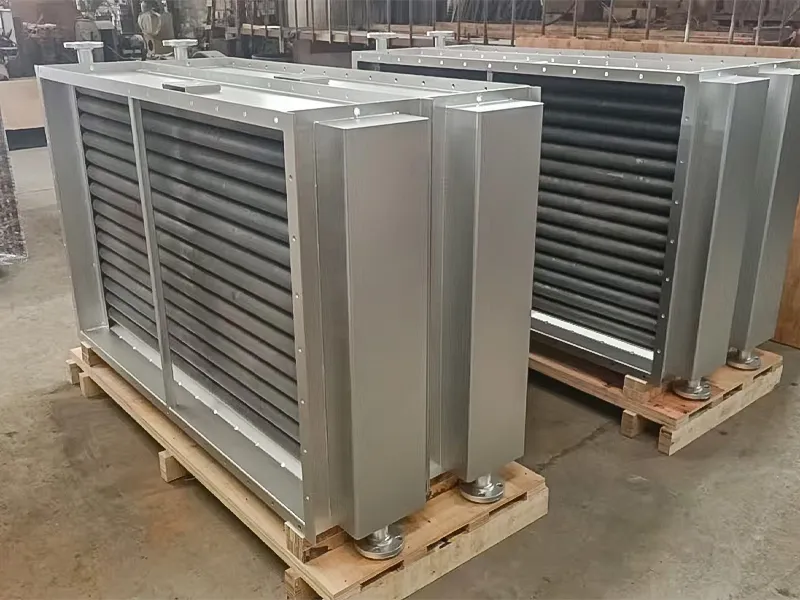

Country: Sri Lanka
Main Material: Carbon Steel Tube /Alu. Fins

Air-Cooled vs. Water-Cooled Heat Exchangers
Which One to Choose?
● Air-cooled systems are recommended for water-scarce or high-temperature regions, offering low maintenance costs and zero water consumption.
● Water-cooled shell-and-tube exchangers are ideal when lower outlet temperatures, compact installation, or reliable water supply are required.
● We also offer hybrid (dry/wet) air-cooled systems for enhanced performance in hot climates.
Supporting Products:
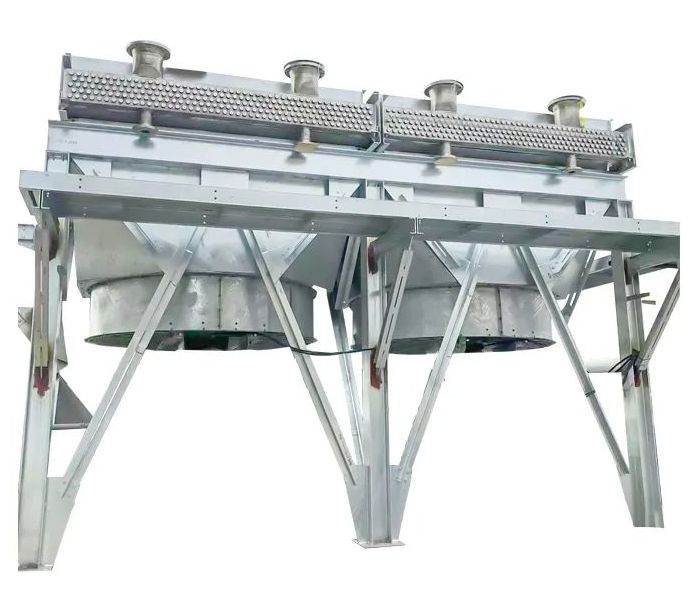

● Air Fin Cooler / Dry Cooler
● Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
● Plate Heat Exchanger
● Hybrid Cooling Systems (Dry + Spray)
Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers (Dry Coolers, Air Fin Coolers)
Advantages
● Environmentally friendly: no water consumption, no thermal or chemical pollution
● Site flexibility: suitable for arid areas or water-scarce regions
● Easy maintenance: corrosion-free, scaling-free, long service life
● Lower operating costs: air has low resistance and no treatment cost
● Passive cooling: retains 30–40% natural cooling even when power is off
Limitations
● Cooling is limited by dry-bulb temperature; it cannot cool below ambient
● Requires a larger footprint due to low air-side heat transfer
● Affected by weather: wind, sunlight, and seasonal changes impact performance
● Noise: due to fans and airflow
● Requires finned tubes and specialized fan systems
Shell-and-Tube Water-Cooled Heat Exchangers
Advantages
● High cooling efficiency: outlet temperature can approach wet-bulb conditions
● Compact design: smaller footprint, easily integrated into tight spaces
● Stable performance: unaffected by ambient temperature fluctuations

● Quiet operation: no fans, minimal noise
Limitations
● High water consumption and pollution risk
● Needs water source, pumps, pipelines, and treatment systems
● Corrosion & scaling: frequent maintenance and chemical treatment required
● Total shutdown upon power failure
● Biological growth risk in warm climates